It’s always made sense on an intuitive basis. Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) include spinning platters, moving arms with read/write heads, motors to power things, and gears to control action. SDDs are made entirely of circuitry: no moving parts. Thus, it’s compelling to assert that SDDs should be more reliable, and less prone to failure than HDDS. And indeed, the latest 2022 Drive State report from online backup and storage provider Backblaze weighs in on this topic. As I read it, that Backblaze data confirms SSD trumps HDD reliability.
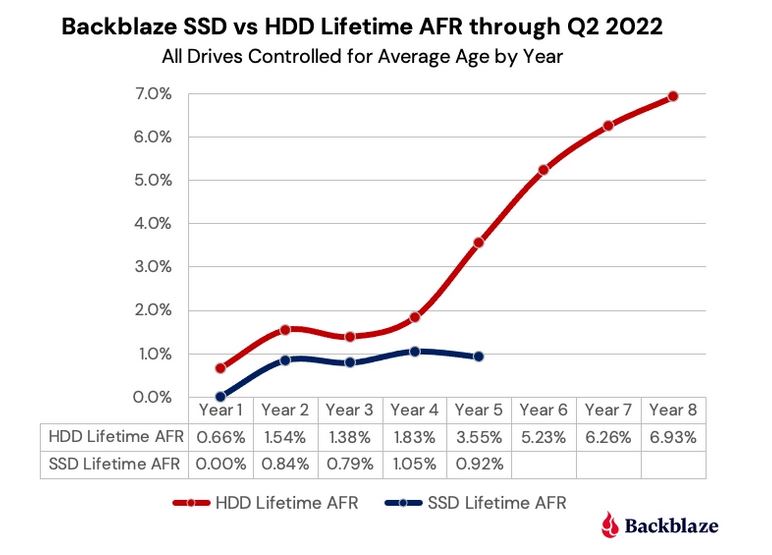
The lead-in graphic shows 4 years’ worth of SSD data vs. 8 years for HDDs for boot drivers in their thousands of datacenter based servers. Whereas there’s a dramatic upward knee in the curve for HDDS between years 4 and 5 (from 1.83% to 3.55%), failures actually dipped for SDDs during that interval (from 1.05% to 0.95%). Interesting!
How Backblaze Data Confirms SSD Trumps HDD Reliability
The afore-linked report explains that boot drives function in multiple roles on the company’s plethora of storage servers. They store log and temprorary files; they maintain storage holdings based on each day’s storage activities and volume. The disparity in the number of years for which data is available comes from later adoption of SDDs as boot drives at BackBlaze. That practice started in Q4 2018. Today, all new servers boot from SSDs; older servers whose HDD boot drives fail get SSD replacements.
The numbers of SSDs keep going up, too. The end-of-year 2021 SSD report encompassed 2,200 SSDs. By June 30, 2022, that count grew to 2,558. Failure rates for such devices show much lower numbers than for HDD (see the tables labeled Backblaze SSD Quarterly Failure Rates in the latest report for more detail). Models included come from the following vendors: Crucial, Dell, Micron, Seagate and WDC.
Note: the report itself says:
For any given drive model in this cohort of SSDs, we like to see at least 100 drives and 10,000 drive-days in a given quarter as a minimum before we begin to consider the calculated AFR to be “reasonable”.
The real news, of course, is that quarterly, annualized and lifetime failure rates for SSDs are significantly lower than for HDDs, based on Backblaze’s own long-running data collection. Thus their conclusion comes with the weight of evidence “…we can reasonably claim that SSDs are more reliable than HDDs, at least when used as boot drives in our environment.”
Good stuff! As for me, I like SSDs not just because they’re less prone to failure. They’re also FAST, if more expensive per storage unit than spinners.
Compared to a traditional hard drive disk, an SSD is considered to be faster and more reliable in terms of data storage and management as it uses NAND flash memory instead of mechanical platters. The amount of data that an SSD can write for a declared period of time measures its endurance.
Failure rates are still failure rates though — aren’t they? If Backblaze has to pull a unit out of service, the impact is about the same irrespective of device type. Good, accurate observations, though…
Thanks for posting,
–Ed–