A recent Windows news story reports that “KB5012643 for Windows 11 breaks .NET Framework 3.5 apps” (WindowsReport). This raises some interesting questions for Windows 11 users. For some, it apparently renders certain apps inoperable. Indeed, the bug highlights the value of checking Windows DotNET versions installed on a given PC.
So I did a little research, and learned there are at least two methods to run this info down. In fact, MS offers a multi-page Docs item that explains how to do it using PowerShell. Belgian-based software developer (and former MVP) Nick Asseloos’ ASoft company goes another way. It offers a free download named .NET Version Detector. Its output provides the lead-in graphic for this story.
What Checking Windows DotNET Versions Installed Tells You
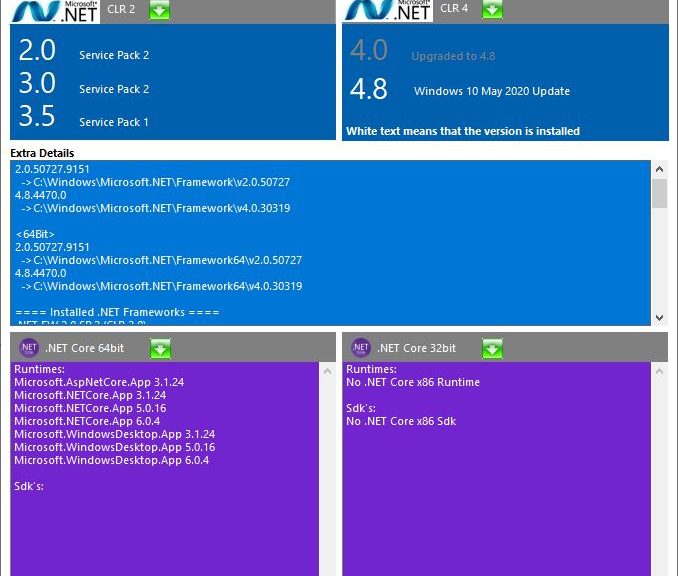
As you can see by examining the lead-in graphic. the detector provides information of several kinds, conveniently listed in order from top to bottom by row:
Row1: Versions of the MIcrosoft .NET Framework Installed. In my example, it shows older versions to the left (2.0, 3.0, and 3.5, with SP levels),and current versions to the right (4.8, with latest update level).
Row2: Extra Details show the folder locations for the various frameworks installed. It also shows names and levels for frameworks installed as well (mostly relevant to 4.x versions), plus languages and updates (mostly a bunch of KB article identifiers).
Row3: .NET Core versions installed for 64-bit (left) and 32-bit (right) enviornments. Given my machines all run Windows 10 or 11, 32-bit is mostly MIA.
How ‘Bout Going the Other Way ‘Round?
OK, we know now how to determine what .NET versions are installed on a Windows PC. What about figuring out which applications use some specific .NET framework? That’s a bit trickier. The only sure-fire method I could find was to fire up SysInternals Process Explorer. There’s a tab named “.NET Assemblies” that shows up whenever a process that includes same gets highlighted.
This means you can find out which .NET versions are in use primarily by observation and inspection. Stack Overflow has an article that explains how to automate this process for managed processes using C# or PowerShell. I’ll leave that as an “exercise for the reader” for those inclined to work out to that extent!
[Note: this story gives a shout out to the redoubtable Martin Brinkmann at Ghacks, whose 2014 story (updated 2018) introduced me to ASoft .NET Version Detector. Nochmals vielen Dank! (Thanks very much again!)]