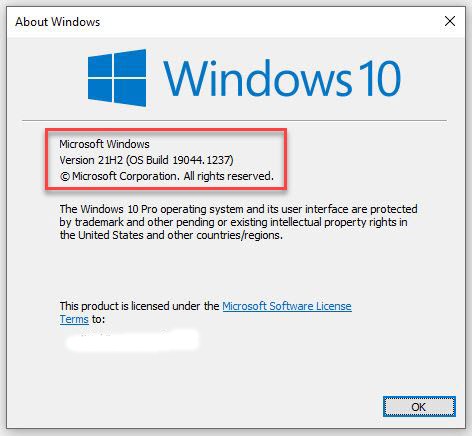
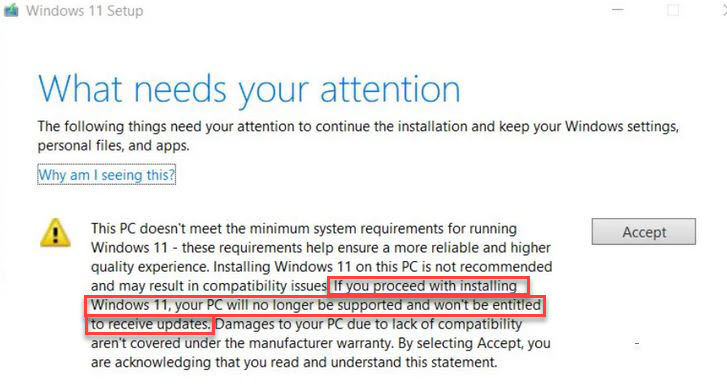
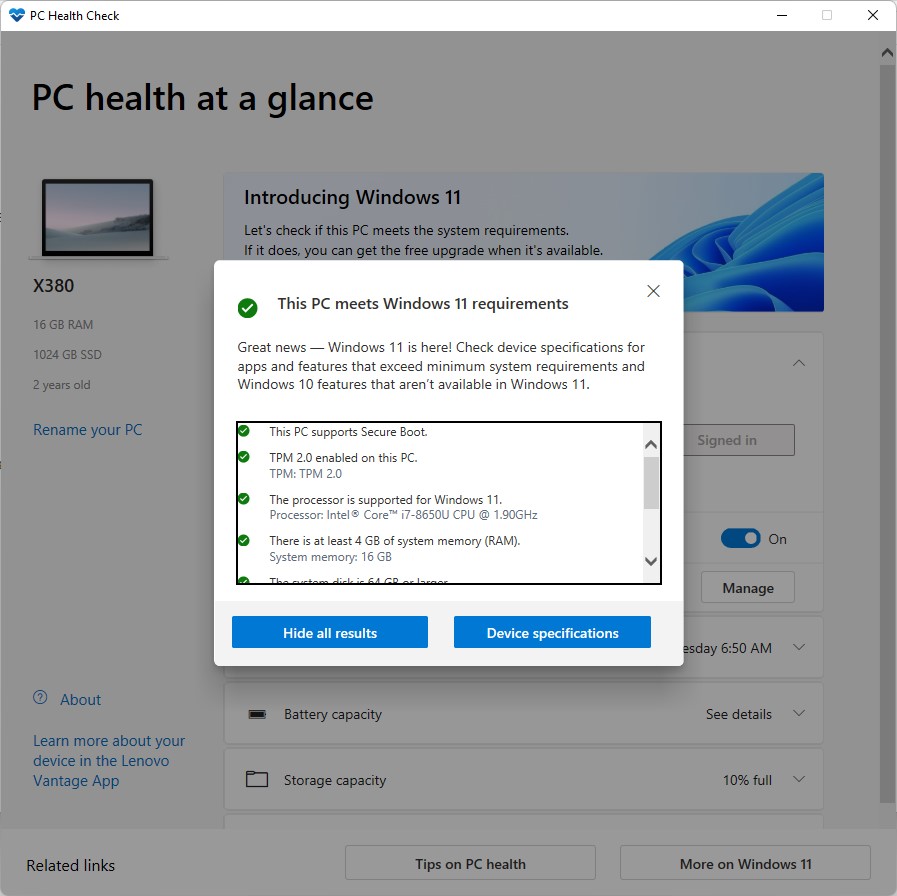
As I write this item on the morning of October 4, I’m sure I’m not the only person anticipating tomorrow’s General Availability release for the lastest Windows version. But with the approaching October 5 onset of Windows 11: Revisiting Microsoft Gradual Rollouts should help readers properly craft their expectations.
For Windows 11: Revisiting Microsoft Gradual Rollouts Sets the Stage
The watchwords here are “gradual rollouts.” This means that MS will start the release of Windows 11 with a trickle. The first machines to get an upgrade offer will be those for which telemetry shows no upgrade problems. That trickle will gradually increase over time as known problems get solved.
Another source of upgradability comes from so-called “seekers.” Seekers are those who grab upgrades via download without waiting for an offer from WU. Their telemetry will also show other machines that offer reasonable expectations of a positive upgrade experience. They, too, will start to get offers.
How Long to Get from Trickle to Flood?
If recent Windows 10 version upgrades are any indicator, it can take six months to a year before the gradual rollout switches over to wholesale access. It’s truly a data-driven exercise, in which telemetry provides the input to steer users into a new version “at the right time.”
My own track record is one of less patience, more WTF. I’ve tried to let WU dictate the pacing of upgrade offers for previous version. But I’ve not once been able to let WU drive upgrades for all six or seven of my production machines. These are the ones that run the current version of Windows 10, whatever it may be. Of that half-dozen, at least 5 meet Windows 11 requirements and will get the offer at some time or another.
Once again, I will wait awhile to see when that offer might come. It might take MS more than a month to extend it to my newest PCs (11th gen Intel and Ryzen 5800X CPUs). If so, I’ll do an ISO-based install from setup.exe soon thereafter. I’m just not that relaxed about making the 10-to-11 transition, I guess…
Stay tuned: I’ll keep you posted.