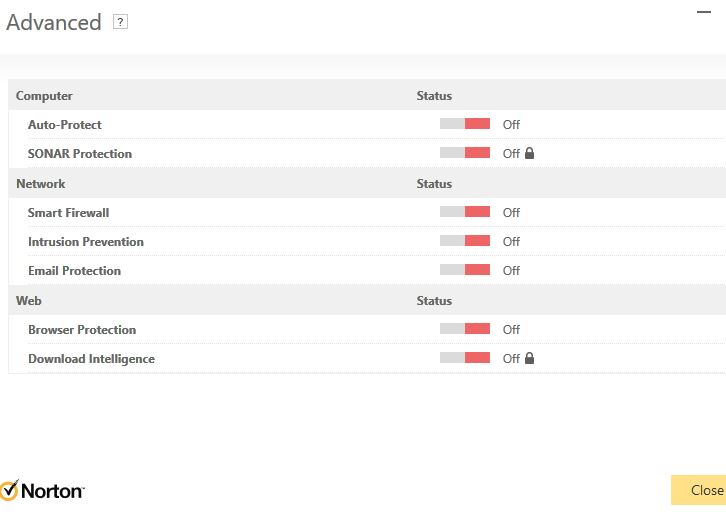
Here’s an interesting issue — and another reason why I’m abandoning Norton security after I get my new PC built. I just tried to update CrystalDiskInfo and I couldn’t make it work. Norton data protection prevented the installer from — of all things — deleting old .bmp files for icons and graphics, to replace them with new ones. Even after I turned everything in Norton off for which it provides controls, the &*%$$ program still got in the way. Then it occurred to me: when security stymies update remove and reinstall still works. So that’s what I did, and that’s how I got it to work. Sheesh!
When Security Stymies Update Remove and Reinstall for New Version
Because update operations wouldn’t proceed even after disabling the auto-protect, firewall, and AV functions (see lead-in graphic), I was faced with two alternatives. First, I could completely uninstall Norton and then update. Or second, I could uninstall the old CrystalDiskInfo version, and then cleanly install the new one. Because it was so much less time and labor intensive to undertake the latter, that’s what I did.
But man! I *HATE* it when security software gets in the way of authorized, valid update behavior and I can’t make it stop. By itself, that’s enough to have pushed me to get rid of Norton. But I’d already planned to do that anyway. I still use the password manager (which is a pretty good one), but I have no use any longer for the rest of the suite.
It just goes to show you: when it comes to maintaining Windows PCs, there’s always something lurking in the background ready to strike. This time, I got stung just a little. But sometimes, workarounds are less obvious, or less easy to find and apply. This time, I got lucky…