Oh boy! I found myself fighting several interesting Windows issues yesterday. Long story shot: my unscheduled restore drill ends well at the final conclusion. But first: I have to rebuild my boot configuration data and create new Macrium Rescue Media before I can actually boot into the restore environment. It’s always something, right? Let me tell you what that meant yesterday…
After Initial Obstacles, Unscheduled Restore Drill Ends Well
First, a benediction: I remain grateful that I take a scheduled backup at 9AM every morning, 365 days a year. If it weren’t for that backup, I would have been in real trouble. Indeed, I tried an in-place upgrade repair install during my recovery sequence. That’s when I observed that while it fixes OS files perfectly, it does not fix self-inflicted file system or Registry issues.
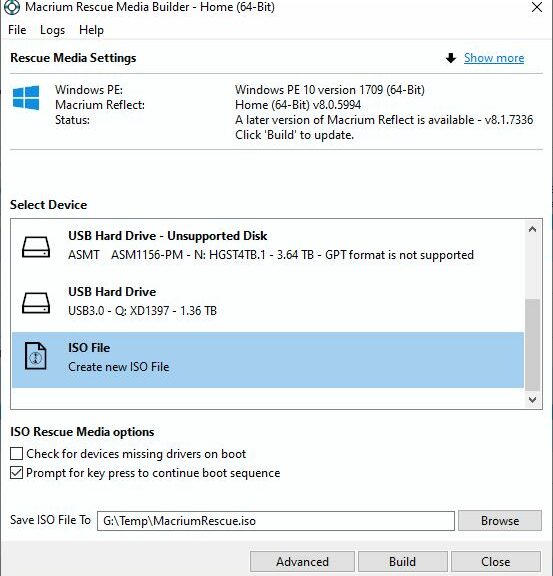
My first hint of difficulty came when I tried to restore my 9 AM backup. The timestamp on that file is actually 9:52 so that tells you how long it took to complete as a background task. Turns out my Macrium Rescue Disk wouldn’t or couldn’t boot successfully. It would simply get as far as the bootloader, spinning balls against a black screen, and never get any further. Yikes!
BCD Complications
Next, I unthinkingly added a Macrium Rescue Media element to the boot menu. This did neither harm nor good. But alas, it extended the time it takes to reboot by a good 2 minutes. In a situation where I was rebooting a LOT, that really didn’t help things much. Sigh.
Note: when I did eventually restore the 9AM backup it perforce rewrote the whole boot/system disk, so that little BCD change got undone. Yay! I really don’t need it anyway…
Restore Requires Working, Bootable Rescue Media
Eventually, I turned to the excellent Macrium user forums to find insight on my hung restore. I switched from a faster, bigger NVMe drive in a USB enclosure, to an older, slower, and smaller USB flash drive. That ultimately did the trick.
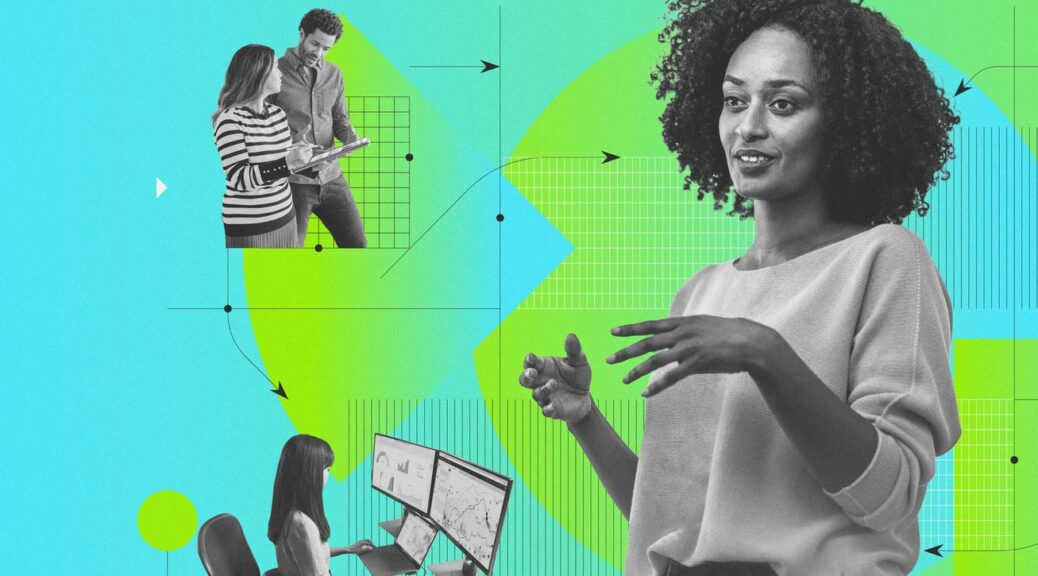
For some reason, I had to build the rescue disk twice to get it to work. I may have forgotten to check the “Check for devices missing drivers on boot” checkbox the first time around. I was sure to check it on the second try (see lead-in screencap: it’s unchecked by default). After that, the Macrium restore operation proceeded automatically and the process ground through to its lengthy conclusion.
It had been long enough since I did a restore that the time required came as a quasi-revelation. All told, it took about 70 minutes from firing off the restore inside the damaged Windows 10 installation to return to the desktop inside the 9AM image snapshot. That’s quite a bit longer than the 14 minutes or so it takes to backup in single task mode (52 minutes as a background task).
But wow, was I relieved to get over that hump! And now, I have working proof that my backup/restore regime produces its intended outcome. It was an interesting ride in the meantime…