Here’s an interesting thread emerging from the Windows press. A growing number of outlets are reporting that Microsoft’s own NVMe drivers run slower than their Win10 counterparts on identical (and other hardware). If Windows 11 sports slow NVMe driver, what can users do? Not much, it turns out, unless they can run a third-party driver instead (e.g. Samsung NVMe Controller). For good coverage on this topic, see Taras Buria’s recent WinAero story “Windows 11 apparently slows down NVMe SSDs.” It cites a range of interesting and informative original sources.
If Windows 11 Sports Slow NVMe Driver, Then What?
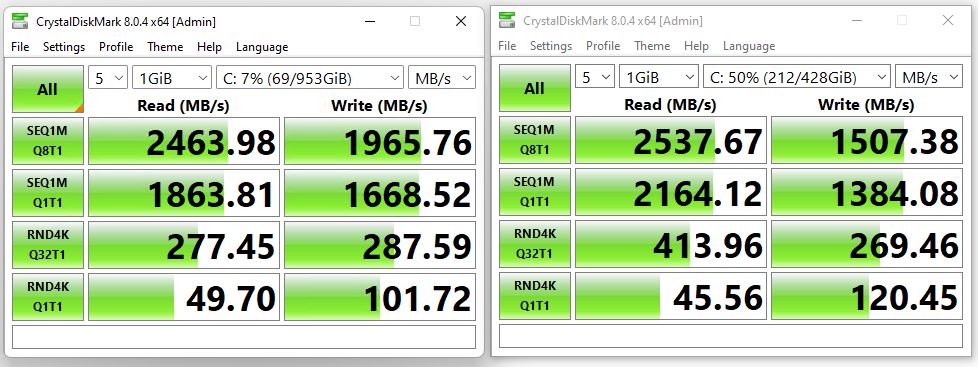
What appears to be affected is the OS boot/system drive (usually C:, where Windows itself resides). Some independent tests show that other non-OS partitions don’t suffer performance degradation. But OS partitions could suffer from reductions in random read/write speeds of 50% or worse. For grins I compared CrystalDiskMark stats from my 11th gen Lenovo X12 Hybrid Tablet running Windows 11 to my 6th gen home-brew Z170-based desktop. The former has a WD SN530 1 TB SSD, while the latter has a Samsung 950 1 TB SSD.
As you can see in the lead-in graphic, the newer Windows 11 unit is a bit slower on most readings than the older Windows 10 PC. Indeed QD32 random reads are about 1/3 slower. That said, random writes of the same ilk go the other way (but with a less-than-7% delta). For random reads/writes with QD1, 11 edges 10 on writes by just over 9%, and vice-versa for reads by just over 15%. Kind of a wash, if you ask me.
What This Means for Upgrade Plans
MS has acknowledged that the issue is known to them and that they’re working on a fix, ETA unknown. Some reports aver that this phenomenon justifies postponing upgrades until a fix is in. My own experience with Windows 11 has been uniformly positive so far, NVMe performance observations notwithstanding. I’d recommend rethinking upgrades on PCs with heavy I/O workloads (e.g. CAD, AI, data analysis, and so forth). But for routine personal or productivity computing, it doesn’t really seem to make a noticeable difference.
I’ll be watching this issue as it unfolds. Count on me to let you know when this situation changes. Given the importance of NVMe to modern computing workloads, lots of people will no doubt follow this carefully and closely.
Note Added December 10: KB5007262 Fixes Issue, But…
KB5007262 should be installed as part of the upcoming December 14 updates for production Windows 11. It came out for Beta/Dev Channel users in November (ditto for production versions, as a Preview Update on November 23). Indeed, it seems to fix the performance issues. According to this WinAero story, the MS bugfix info for the KB5007262 announcement includes the following text:
“Addresses an issue that affects the performance of all disks (NVMe, SSD, hardisk) on Windows 11 by performing unnecessary actions each time a write operation occurs. This issue occurs only when the NTFS USN journal is enabled. Note, the USN journal is always enabled on the C: disk.”
And indeed, on my X1 Extreme laptop (8th gen i7, Samsung OEM 512GB NVMe SSD, 32 GB RAM) speeds are where experience teaches me they should be. According to the afore-linked story, this fix applies to all versions of Windows 11 except Dev Channel. As far as I can tell, that version remains subject to the slow-down. I’m looking for some additional word from MS on this topic. Hopefully, they’ll fix it there soon, too. Stay tuned!