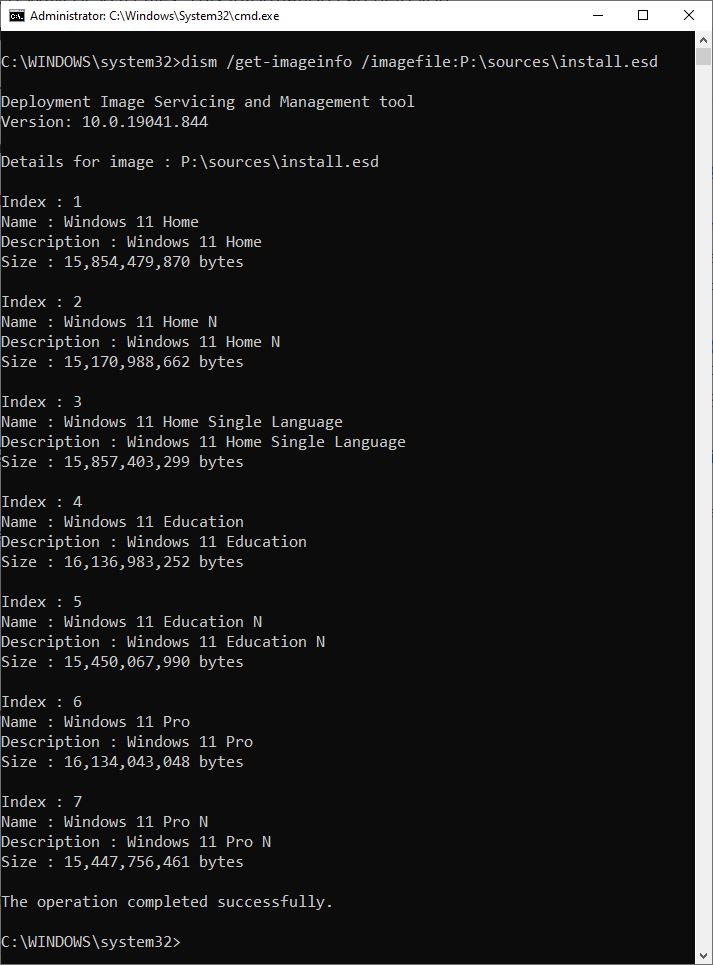
If you know where to look, the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK) is now out for Windows 11. Indeed, you can find it in MS Docs at Download and install the Windows ADK. That’s why I assert that the Windows 11 ADK is now available in this item’s title. What does this buy you and your organization? I’ll explain…
If Windows 11 ADK Is Now Available, Then What?
The ADK includes collection of potentially useful and valuable tools designed for at-scale Windows deployments. These include access to:
- WinPE, the Windows Preinstallation Environment that provides runtime support before an OS has loaded. It’s used to support Windows installation and also provides the foundation for WinRE (Windows Recovery Environment). Basically, it’s a stripped-down and self-supporting portable version of Windows (11 in this case). Note: WinPE is a separate add-on to download and install after installing the ADK.
- Volume Activation Management Tool (VAMT): works with Windows Office and other Microsoft products for volume and retail activation using Multiple Activation Keys (MAKs) or the Windows Key Management Service (KMS). Works as an MMC snap-in with the Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
- User State Migration Tool (USMT) delivers a customizable user-profile migration capability that can capture user settings for Microsoft office versions 2003, 2007, 2010, and 2013 (separate tool for 2016 also available). The tool covers a broad range of migration scenarios (described here).
- App-V (Application Virtualization) is still supported, but MS calls out EOL for April 2026, and now recommends using Azure Virtual Desktop with MSIX app attach instead.
From a different perspective, the ADK includes support to assess, plan for and execute large-scale Windows deployments. Assessment comes from the Windows Assessment and Windows Performance toolkits. Deployment tools include WinPE, Sysprep, and other items that can customize and distribute Windows images.
It’s Early in the Lifecycle…
Organizations are mostly still considering Windows 11 deployments, though some pilots are underway. Grab yourself a copy of the new ADK and you can get to know it, as your organization starts pondering and investigating its Windows 11 options and timetables. Cheers!