I’m a regular at ElevenForum.com and TenForums.com. I try to read all new threads there daily, but probably average two out of three over the long haul. This morning, I saw a post at ElevenForum entitled “Services to Disable Windows 11.” My immediate response was “Why bother?” These days, Windows is self-tuning and runs pretty lean — especially Windows 11. That’s why I assert “Modern Windows Service Tweaking Is Counterproductive.”
More on Why Modern Windows Service Tweaking Is Counterproductive
One especially interesting analysis in response to the original poster’s list of prospective services to disable is especially illuminating. It comes from long-time Guru-level user @Bree, who says:
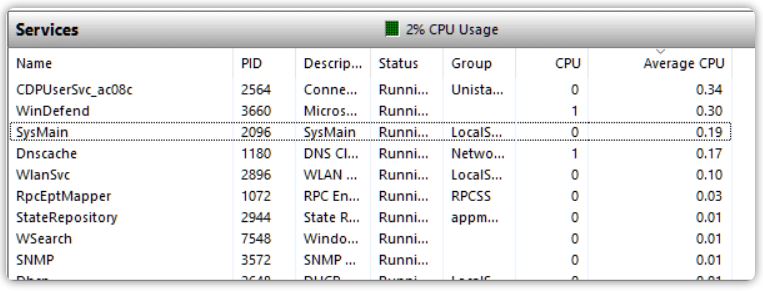
If you open Resource Monitor, look at Services on the CPU tab and sort by Average CPU, then you’ll find that of your list SysMain has the highest CPU use – of less than 0.2%. In fact my total CPU use by all running services is just 2%.
The general point is that while it’s theoretically possible to trim down the default set of services and processes to lighten the Windows load, the gains are small. In addition, turning things off that Windows thinks should be turned on can occasionally cause stability problems (read the whole thread for more details).
The Black Viper Perspective on Tweaked Services
BlackViper.com has been active on the Internet recommending such tweaks since the days of Windows 95/98. The last set of such tweaks for Windows 10 on his site is for version 1803 (as in March, 2018, almost four years ago). There are no such tweaks for Windows 11, period. To me, this says even a long-time, professional-grade tweaker no longer finds it worthwhile or rewarding to do this kind of thing with modern Windows versions. I couldn’t agree more, and stick by my title for this piece! ‘Nuff said.