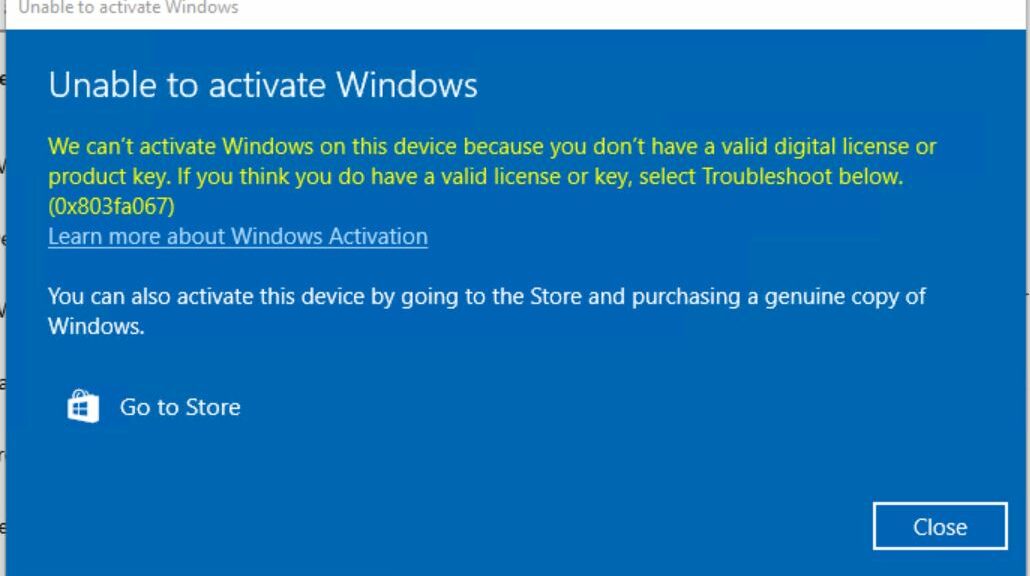
On September 29, I reported that one couldn’t upgrade from Windows 7 or 8.1 to 10 or 11 any more. But, one could still activate a clean install of 22H2 using their keys. As of yesterday, I can conclusively say: “No more!” I used an older key to get through install yesterday. But this morning, the desktop said Windows 10 needed activation. Thus, I’m now convinced the Win7/8 key loophole closes at long last.
More About Win7/8 Key Loophole Closes
Interestingly, the activation servers have to grind for quite some little while. It takes 25-35 seconds before they come back to disqualify older keys. If you hand them a newer one (I tried both retail and MAK keys for Windows 10 and 11) activation comes in 3-4 seconds. There’s obviously a lot of behind-the-scenes checking going on.
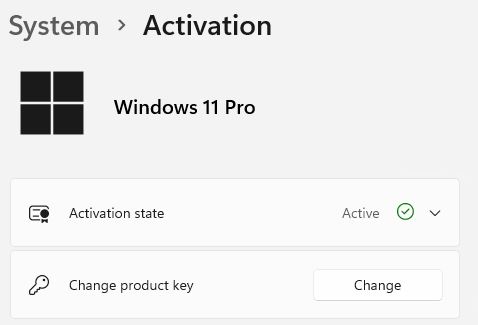
That said, the Windows 11 Pro VM I stood up last week using a Windows 7 Ultimate key is still running. In fact, it still shows “Active” as its current activation state. I’m speculating freely when I say this, but that tells me the loophole has been closed later, rather than sooner. We’re unlikely to get official commentary from MS on this one way or the other, so take my supposition for what it’s worth!
It’s Been a Long Time Coming…
Ever since the door officially closed on upgrades from and activations of older keys back in 2016 (7 years ago), we’ve all known this day was coming. Now it’s here. Gosh, it was terrific while it lasted, though, because I never had to worry about running out of keys for throwaway VMs and test installs. I guess we’ll all have to be more careful going forward. I’ll also make more frequent use of the various 90-day eval VMs that MS generally makes available as well.