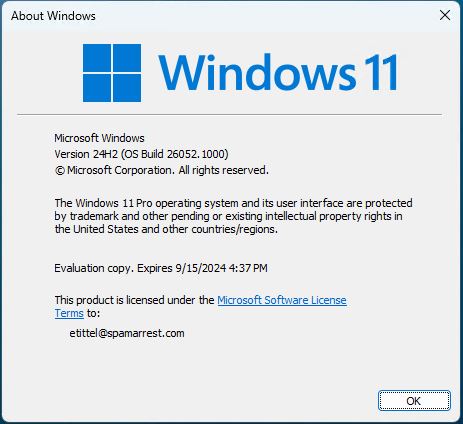
OK, then: the ‘net has been abuzz since last week as upcoming Windows 11 24H2 requirements come clear. Indeed, that OS won’t run on processors that don’t support the POPCNT instruction . IMO this POPCNT fuss is more fizzle than it is a major obstruction. Let me explain…
Why Say: POPCNT Is More Fuss than Fizzle
The POPCNT instruction has nothing to do with stack processing as its name might suggest. Rather, it counts up all 1-values in a binary sequence. It’s part of the SSE4.2 instruction set. These were introduced in 2008 to both AMD and Intel processors — namely:
- AMD K10 (codename Barcelona), released in April of that year
- Intel (codename Nehalem), released in November same year
That means the oldest processors that DON’T support SSE4.1 (and POPCNT) are more than 15 years old. Not terribly suitable for running Windows 11 anyway and likely to fail owing to lack of support for TPM, Secure Boot, and other reasons as well.
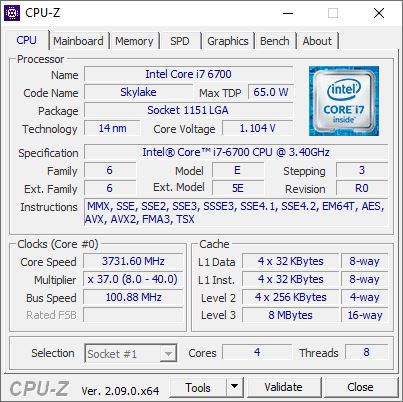
You can use Franc Delattre’s excellent CPU-Z tool to check your CPU to see if it supports SSE 4.2 or not. Check the lead-in graphic next to “Instructions.” It pops right up even on my 6th-gen 2016 vintage Skylake CPU (still running Windows 10 BTW).
For all but the most diehard long-haul PC users running a machine more than 5 years old is pushing things (and 15-plus years is highly unusual). This very Skylake is my oldest at 8 years, and it’s due for retirement soon, soon, soon.
WTFuss? No Workaround
The problem with POPCNT is that it’s absolutely, positively mandatory for 24H2 to work. Whereas the other impedimenta — e.g. TPM, Secure Boot, UEFI and so forth — have all been cleverly worked around, there’s no known (or likely) workaround for this gotcha. Thus, older PCs that have been shoehorned into Windows 11 upgrades will not be able to advance past the 23H2 upgrade level. Hence such fuss as has emerged in the blogosphere since this news came out last week.
My best guess that that less than 1% of PCs in the US (and perhaps 5-8% of PCs elsewhere, mostly outside the first world) might be subject to the POPCNT limitation. Just another sign that even here in Windows-World, time keeps marching on.