By default, Windows 10 and 11 both turn on restore points (RPs). These may be used to return an OS environment back to a prior state. The OS typically shoots one RP daily, and takes one as it starts the WU process. In addition, app developers may include taking an RP snapshot early on during their own install processes. All this said, there are plenty of Restore Point pros & cons.
What Are Restore Point Pros & Cons?
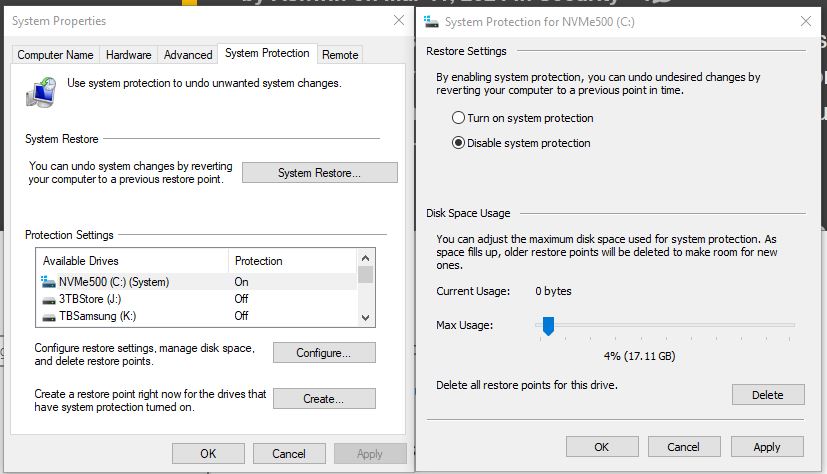
These days you reach Restore Points through the System Protection tab in the System Properties window in Control Panel. Interestingly enough, you have to navigate through Settings > System to get there. Once you find what you’re looking for (see lead-in screencaps) you can enable or disable RPs, and also allocate a maximum percentage of the system/boot disk which these system snapshots can occupy.
RP Pros
RP’s positives include the following:
- Convenience and ease of use: you can create an RP manually with a few mouse clicks, and it takes little time to complete one. It’s also fairly easy to revert to a Restore Point using either Windows built-in tools or one of my faves (it’s an oldie, but a goodie): System Restore Explorer. It tool 33 seconds to create one on my i7Skylake desktop, and 1:05 to restore same on that PC.
- Provides a simple layer of system protection: can easily revert Windows to undo update, app or application, and driver changes. This is faster — but more limited in scope — than even the fastest image backup restore. As a knock-on effect: this can also undo software or library conflicts (after adding an app or application, or a new .NET version, or something else that’s similar).
- Some cleanup when removing new software: This might be somewhere between a pro and a con. Restoring an RP does result in removal of executable files and dlls added when installing apps. But shortcuts, preferences, and other files (including home folders — e.g. inside C:\Program Files or C:\Program Files (x86)) remain intact.
RP Cons
By contrast, RP’s negatives include:
- No antivirus protection: restoring an RP won’t necessarily eliminate triggers for or stealth executables that cause malware infections. Thus malware can return even after using an RP.
- No data file backup: RP copies the contents of the system volume shadow using the Volume Shadow Service (aka VSS). This does not include data files by intention. So RP provides no data restore capability (see the note at the end of this story for a 3rd-party tool that does provide such capability, however).
- New user accounts are not protected by RP: if you define a new user account after the point in time at which an RP shapshot is created, those accounts will no longer exist when that RP is restored. That said, the User files for that account will persist. IMO, this is a kind “worst of both worlds” situation. Sigh.
My Net-Net Is: Don’t Rely Solely on RPs
Reading through the previous plusses and minuses, it’s pretty easy to see that RPs can have value in a limited set of circumstances. But they’re no substitute for a recent image backup, and they’re no panacea for solving non-trivial Windows issues or problems.
I don’t use RPs much myself anymore myself (though I did in the Vista and Windows 7 eras). These days I rely mostly on in-place upgrade repair install for semi-serious to serious troubleshooting, and a clean install (or image restore) for outright system failures and boot problems. It’s also my repair of last resort when nothing else will produce a working Windows instance. Go figure!
Note Added March 19: More Madness
I got a comment from TenForums.com and ElevenForum.com regular “Old Navy Guy” (ONG) this morning reminding me that the NirSoft ShadowCopyView tool does allow users to view and copy certain data files from a VSS snapshot. This *does* allow access to user files and folders and adds to what you can recover from such a snapshot.
I totally forgot about this tool, and am glad to be reminded of same. More important, I’m grateful to have the chance to point this out to you, dear reader — and to make that tool known and possibly useful for you. AFAIK, this capability applies only to files and folders in the Users folder hierarchy, so if you keep stuff on a data drive — as I do — it won’t help much, or at all. But it could still be helpful nevertheless. Cheers!
Note Added March 21: Including Other Drives
Another Homer Simpson moment has come and gone for me. ONG commented again to remind me that ShadowCopyView does data drives, too. I initially wondered how VSS could accommodate drives other than the C: (boot/system) drive where the OS and other key stuff lives. Then it hit me: you must enable RP protection on those drives, too. Here’s an illustrative screencap:
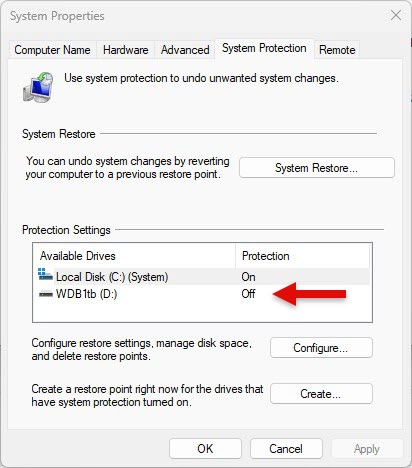
Turn on Protection for the D: drive so it gets VSS snapshots, too.
Maybe there’s more to this protection scheme than I originally gave it credit for. It took 12 seconds to capture an RP for my C: drive and 13-14 seconds for my D: (Data) drive on a Lenovo ThinkPad X380 Yoga. WizTree says C: contains ~80GB of data, while D: contains ~400GB. So it is indeed remarkably fast. And with VolumeShadowCopy providing access to contents, it provides workable file and folder level access to bring back items one-at-a-time or as portions of a target drive’s file hierarchy. Good stuff!